Lymphoma is a malignant tumor originating from lymphatic tissue, including two major types: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Lymphoma can invade any part of the body, with diverse clinical manifestations, usually characterized by swollen lymph nodes, fever, weight loss, night sweats, etc. Although the exact cause of lymphoma is unknown, it is generally believed to be related to infection, immunity, environmental factors and genetics. The number of new cases of lymphoma is increasing worldwide. Data show that there were 589,600 new cases of lymphoma worldwide in 2018.
Lymphoma is a malignant tumor originating from lymphatic tissue, including two major types: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Lymphoma can invade any part of the body, with diverse clinical manifestations, usually characterized by swollen lymph nodes, fever, weight loss, night sweats, etc. Although the exact cause of lymphoma is unknown, it is generally believed to be related to infection, immunity, environmental factors and genetics. The number of new cases of lymphoma is increasing worldwide. Data show that there were 589,600 new cases of lymphoma worldwide in 2018.
Early symptoms of lymphoma include painless swollen lymph nodes and unexplained fever. Swollen lymph nodes may occur in the neck, supraclavicular, axilla, groin and other parts. If compression of adjacent organs occurs, it will also cause corresponding symptoms. Systemic symptoms of lymphoma include fever, night sweats, weight loss, and possible symptoms such as skin itching and fatigue.
The treatment of lymphoma mainly relies on chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and the specific plan depends on the type, stage and prognostic factors of lymphoma. Among them, Hodgkin's lymphoma is mainly treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, while the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma focuses on chemotherapy. For relapsed and refractory cases, DHAP or DICE regimens can be used for rescue treatment, followed by high-dose chemotherapy combined with autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
The prevention of lymphoma is mainly to avoid infection and improve immunity. At the same time, genetic and environmental factors also need to be paid attention to. In population surveys and early diagnosis, laboratory tests such as neurological examinations, blood routine tests, serum lactate dehydrogenase, β2-microglobulin determination, and imaging examinations are helpful for the diagnosis and treatment of lymphoma. Adequate examination and timely diagnosis can improve the cure rate of lymphoma and improve the quality of life.
Lymphoma is a group of malignant tumors of the blood system. With the advancement of science and technology, the classification of lymphoma has become more and more detailed. Now there are dozens of lymphomas, with different types and different biological behaviors. Some have a long course and good prognosis, while others are invasive, progress quickly, and have a relatively poor prognosis.

Symptoms
The clinical manifestations of lymphoma are mainly painless lymphadenopathy and systemic symptoms such as fever, night sweats and weight loss.
Early symptoms
Different types of lymphoma often present with painless lymphadenopathy as the first symptom; unexplained fever is also one of the common first symptoms.
Typical symptoms
Lymph node enlargement
The most common painless progressive enlargement of cervical and supraclavicular lymph nodes in lymphoma patients is the axillary and inguinal lymph nodes. When the progression is rapid, it can fuse into a mass and adhere to the surrounding tissues.
If the enlarged lymph nodes compress the adjacent organs, it can cause corresponding symptoms. Masses in the mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes can cause symptoms such as chest tightness, chest pain, and dyspnea. Masses in the abdominal cavity can cause abdominal pain, intestinal obstruction and other symptoms.
Systemic symptoms
Hodgkin's lymphoma
Patients usually have no obvious systemic symptoms at the time of initial diagnosis. 20% to 30% of patients may be accompanied by fever, night sweats and weight loss (weight loss of more than 10% within 6 months), followed by skin itching and fatigue.
Some patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma present with persistent fever of unknown cause as the onset symptom.
Young women may have local and systemic skin itching. Systemic itching can also be the only symptom of Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Systemic symptoms such as fever, night sweats, and weight loss are more common in the late stage, and systemic itching is rare.
Pain caused by drinking alcohol
Pain caused by drinking alcohol is a special symptom of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Pain at the tumor site often occurs within a few minutes to a few hours after drinking. Such patients often have mediastinal lymph node lesions.
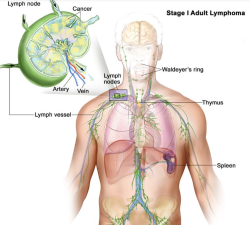
Stages are divided according to the range of lymph node lesions:
Stage I: Involvement of a single lymph node region is stage I, and focal involvement of a single extranodal organ is stage IE;
Stage II: Involvement of two or more groups of lymph nodes on the same side of the diaphragm is stage II, and focal involvement of a single extranodal organ and its regional lymph nodes, with or without involvement of other lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm is stage IIE;
Stage III: Involvement of both upper and lower diaphragmatic lymph node regions is stage III, with focal involvement of extranodal organs is stage IIIE, and involvement of the spleen is stage IIIS, and both are stage IIIE+S;
Stage IV: Diffuse involvement of single or multiple extranodal organs, with or without associated lymphadenopathy, or isolated involvement of extranodal organs with distant lymphadenopathy is stage IV, such as involvement of the liver or bone marrow, even if the lesions are localized, it is stage IV.
Lymphoma treatment includes the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), which are different.
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is mainly treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) has many pathological types and strong heterogeneity. The treatment principles need to be determined according to different pathological subtypes, stages, prognostic factors and treatment goals. Chemotherapy is its main treatment method.
Lymphoma is a malignant lymphocyte tumor. The following are the commonly used drugs for treating lymphoma.
- Chemotherapy drugs: inhibit the growth and division of cancer cells by destroying the DNA and RNA of cancer cells.
(1) COPP regimen: includes cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine and prednisone.
(2) CHOP regimen: includes cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone.
(3) ABVD regimen: includes doxorubicin, bleomycin, vincristine and dacarbazine.
(4) ICE regimen: includes irinotecan, carboplatin and ifosfamide.
(5) EPOCH regimen: includes etoposide, vincristine, cisplatin, erythromycin and pirarubicin hydrochloride.
- Targeted therapy drugs: drugs designed based on surface markers or signaling pathways specific to cancer cells. Such as CD20 antibodies, B cell growth factor receptor antibodies, JAK inhibitors, etc.
- Immunotherapy drugs: enhance the body's immune response to cancer cells by activating the patient's own immune system. Such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, cytokines, etc.
- Radiotherapy drugs: radiotherapy drugs use radiation or other forms of radiation to destroy cancer cells. Such as paclitaxel, imipenem, etc.
- Traditional Chinese medicine treatment: Traditional Chinese medicine treatment can assist in the treatment of lymphoma by regulating the body's immune function and improving physical condition. Commonly used Chinese medicines include herbal medicines with the effects of replenishing qi and blood, clearing away heat and detoxifying.
What are the new advances in the treatment of lymphoma?
For B-cell lymphoma with positive CD20 expression, CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab) can be used for treatment, which can significantly improve the complete remission rate and disease-free survival time of B-cell lymphoma.
In addition, there are some new antibodies, small molecule targeted drugs, immunomodulators, immune checkpoint inhibitors and other new treatment methods for different pathological types of lymphoma. Chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) immunotherapy can achieve good results for relapsed and refractory B-cell lymphoma.
· New antibodies: new CD20 monoclonal antibodies, anti-CD79b-MMAE coupling agents, anti-CD30-MMAE coupling agents, etc. · Small molecule targeted drugs: BTK inhibitors, PI3K inhibitors, proteasome inhibitors, BCL-2 inhibitors, histone deacetylase inhibitors, etc.
However, many new drugs have not yet been launched in China and are still in the clinical trial stage, so suitable patients can enter clinical trials.


