Prostate cancer is to men what cervical cancer is to women, both are diseases that have a great impact. Although most prostate cancers are not fatal, many patients still experience tension and anxiety, which stems from a lack of knowledge about prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is to men what cervical cancer is to women, both are diseases that have a great impact. Although most prostate cancers are not fatal, many patients still experience tension and anxiety, which stems from a lack of knowledge about prostate cancer.
Ethnic groups
The incidence of prostate cancer is high in European and American countries. Studies have found that the incidence of prostate cancer in blacks is as high as 60%, the incidence of prostate cancer in whites is second only to blacks, and the incidence of yellows is relatively the lowest;
High-risk groups for prostate cancer
Middle-aged and elderly men
According to current survey data, the probability of prostate cancer in men under the age of 45 is relatively small, but the incidence of men over 45 is relatively high, especially in men over 60, the incidence of prostate cancer is as high as 1/15;
Family hereditary men
Prostate cancer has a great relationship with heredity. People with prostate cancer in the family will have a relatively high chance of their children having prostate cancer;
Men with excessive hormones
One of the causes of prostate cancer is also related to hormone levels. If the hormone level in men's bodies is too high, the risk of prostate cancer will be higher;
Other factors, such as obesity, underlying diseases, etc.
Obesity caused by high saturated fatty acids is twice as likely to develop prostate cancer as healthy men. In addition, studies have shown that one-third of cancers are related to long-term stimulation of chronic inflammation.

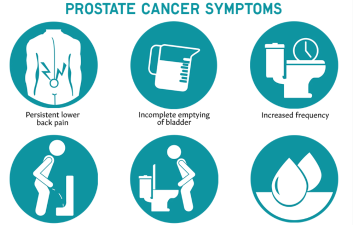
Clinical manifestations of prostate cancer
- Abnormal urination:
When the prostate becomes cancerous, the tumor may compress the urethra or invade the tissues around the urethra, generally leading to urethral stenosis or obstruction, increased urination resistance, and symptoms such as frequent urination, urgency, thinning of urine flow, incomplete urination, and dripping urine.
- Pain in the perineum:
When prostate cancer progresses to a certain extent, the tumor may invade the peripheral nerves, muscle tissue or bones. Stimulation or compression of the above structures generally causes pain in the perineum, lower abdomen, waist and other parts. The nature of the pain may be dull pain, dull pain or severe pain.
- Hematuria:
Tumor tissue grows rapidly, with rich blood vessels on the surface and fragile texture. During urination, the blood vessels on the surface of the tumor may rupture and bleed, and the blood mixes with the urine to form hematuria.
- Weight loss:
Prostate cancer is a wasting disease, and the continuous proliferation of cancer cells requires a lot of energy and nutrients. At the same time, prostate cancer may cause patients to lose appetite, digestive and absorption dysfunction, etc., resulting in the body's intake of nutrients that cannot meet the needs, resulting in gradual weight loss and physical weakness.
- Erectile dysfunction:
Prostate cancer may affect the neurovascular bundle related to erectile function, leading to insufficient congestion of the corpus cavernosum of the penis, thus causing erectile dysfunction.
Prostate cancer is often asymptomatic in the early stage. As the tumor develops, the symptoms caused by prostate cancer can be summarized into two categories:
Compression symptoms
The gradually enlarged prostate gland compresses the urethra, which can cause progressive dysuria, manifested as interrupted urine flow, dripping after urination, and incomplete urination. In addition, there are frequent urination, urgency, pain, increased nocturia, and even urinary incontinence. These symptoms are actually symptoms of prostate hyperplasia. Many patients with prostate cancer think that it is just prostate hyperplasia and do not pay too much attention, resulting in missing the best period.
In addition to urinary tract symptoms, tumor compression of the rectum can also cause difficulty in defecation or intestinal obstruction, compression of the vas deferens to cause lack of ejaculation, compression of nerves to cause perineal pain, and can radiate to the sciatic nerve.
Metastasis symptoms
Prostate cancer can invade the bladder, seminal vesicle, and vascular nerve bundles, causing hematuria, hematospermia, and impotence. Pelvic lymph node metastasis can cause edema of both lower limbs. Prostate cancer often metastasizes to the bone, causing bone pain or pathological fractures, paraplegia. It can also invade bone marrow and cause anemia or a decrease in the whole blood count.
Prostate cancer patients can improve their condition through partial prostatectomy, radiotherapy, etc. under the doctor's operation. During the treatment, they need to eat a balanced diet and eat some apples, cucumbers, eggs and other foods to speed up recovery.
Impact and harm
Prostate cancer is a malignant tumor. If not treated in time, it may be life-threatening. The treatment of advanced prostate cancer is difficult and the prognosis is poor, which seriously affects the patient's quality of life and survival.
Specific details Symptoms
In addition to the above four symptoms, prostate cancer patients may also experience systemic symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue, and loss of appetite. If these symptoms occur, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Three recipes and lifestyle habits
Scrambled eggs with tomatoes: Tomatoes are rich in lycopene and have anti-cancer effects. Cut tomatoes into pieces and fry them with beaten eggs, which is both delicious and healthy.
Green tea drinks: The tea polyphenols in green tea have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which help prevent prostate cancer. After brewing green tea, drink 1-2 cups a day.
Nuts salad: Nuts such as walnuts and almonds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E, which help reduce the risk of prostate cancer. Mix various nuts with vegetables such as spinach and lettuce, add a little olive oil and lemon juice for seasoning, and use it as a healthy side dish.
In daily life, you should also pay attention to the following living habits:
Maintain a regular work and rest schedule and avoid staying up late; drink plenty of water and maintain adequate urine volume to help eliminate harmful substances in the body; maintain moderate exercise to enhance the body's immunity; reduce the intake of high-fat and high-calorie foods and eat more fresh vegetables and fruits.
Prevention and attention
In order to prevent the occurrence of prostate cancer, middle-aged and elderly men should regularly undergo prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing and prostate digital examination. For people with a family history or other high-risk factors, they should be more vigilant. At the same time, maintaining good living habits and a healthy lifestyle is also the key to preventing prostate cancer. Once you suspect symptoms of prostate cancer, you should seek medical attention for examination and treatment in time to avoid delaying the disease.
Conclusion
Although prostate cancer is terrible, as long as we remain vigilant, pay attention to subtle changes in the body, and adjust our lifestyle in time, we can prevent it to a large extent. Remember, health is not everything, but without health, there is nothing. Let us work together to pay attention to men's health and pass on care and knowledge to our relatives and friends. In the face of the challenge of prostate cancer, let us be full of confidence and courage to meet the challenges of the future together.


